1. Territorial Jurisdiction

Law enforcement officials remove filing cabinets and boxes from a building in New York on August 12, 2003.
If a suspected terrorist is in the United States, the answer is easy: The only way to deal with him is to arrest and prosecute him in the civilian criminal justice system. Military detention is not available for citizens or domestic captures. The Bush administration tried it for citizens caught domestically only once, in the case of Jose Padilla, and eventually gave up and tried Padilla in civilian court. The Obama administration has stated that it will use the civilian justice system exclusively both for domestic captures in general and for citizens, wherever our forces get them. So if the suspect is here at home, first, the FBI and other law enforcement agencies will monitor him to learn about the full extent of his activities and gather evidence to determine whether he has in fact committed a crime. And if so, they will arrest him.
2. Arrest, Indict and Prosecute

Employees walk to the Department of Justice in Washington, D.C.
Though it remains controversial, the domestic criminal justice system is actually one of the workhorses of American counterterrorism. Since 9/11, the United States has handled more Americans as criminal suspects than using all other options combined -- both using charges of terrorism itself and using more inchoate charges like conspiracy and material support for terrorism. In addition, a significant number of Americans suspected of involvement in terrorism have been convicted of lesser, sometimes unrelated, charges.
3. Return to the United States

U.S. customs inspectors search passengers' bags on arriving at New York's JFK airport.
If the suspect is overseas the complications begin. Some suspects may be outside of the United States and have plans to return -- concrete, specific plans the government knows about.
Most terrorists camped out overseas, however, are not rushing back, and even when they are, trusting that a suspected American terrorism suspect will return home to be arrested is risky. Locals may tip him off that the United States is seeking him (yes, it is usually a him), or he may decide for his own reasons to delay or cancel his return. In addition, allowing a suspected terrorist on a plane -- even if thoroughly searched -- is nail-biting for officials involved.
So, not surprisingly, it is rare that an individual will be both known to be returning and also allowed to do so. Most of the time, officials cannot simply assume that a suspect will fall into their laps.
4. Wait for Return

A sketch of Jose Padilla appearing at a courthouse in Miami.
Abu Zubaydah, a jihadist logistician, had reportedly told interrogators that he knew of individuals planning to conduct a radiological attack on the United States. Based on this and other intelligence, the name of Jose Padilla came to the attention of U.S. officials and, after Padilla applied for a replacement passport in Pakistan, U.S. officials learned he was traveling home to the United States. While Padilla was initially held in military custody, today that would not happen. A suspect the government knew was on his way home would, like the suspect already here, be detained and enter the criminal justice system directly.
5. Is there a Reliable Ally to Handle the Problem?
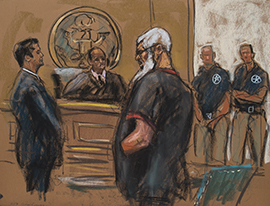
Islamist cleric Abu Hamza al-Masri is seen in this courtroom sketch during a court appearance in Manhattan Federal Court in New York. Masri, who is not a U.S. citizen, was imprisoned in the United Kingdom in 2004 and extradited to the United States in 2012 and is facing a number of terrorism-related charges.
If the suspect is abroad and not headed home, the question of which country he is in becomes important. Is he in a country whose government will reliably keep an eye on him -- and arrest him, if need be? Is that government functional enough to pull off an arrest, or does it lack control over significant parts of its territory? Is it a country that will grossly mistreat the suspect in a fashion that might prejudice his ability to get a fair trial? Is it a country with an extradition relationship with the United States?
The answers to these questions vary a great deal among the many countries in which U.S. nationals suspected of terrorism have taken refuge. If an American is living in Britain, for example, a country with strong legal institutions and a cooperative working relationship with the United States, the issue looks very different from when an American suspect is in the tribal areas of Pakistan -- or the ungoverned areas of Yemen, a country with a history of failure to prevent al Qaeda jail breaks. Americans in Somalia, a country with no functioning government at all, are a different story still. And then there’s Saudi Arabia -- a highly effective police state that has had no trouble arresting American jihadists, but whose treatment of them afterward has required careful monitoring to make sure that statements given were not elicited through torture.
6. When an Ally Will Transfer

U.S. President Obama meets with King Abdullah of Saudi Arabia at the White House in Washington.
When an ally is willing to arrest and transfer a suspect to U.S. custody, suspects inevitably wind up back in criminal-justice land. This is in some ways the ideal solution, as it requires only law enforcement and intelligence cooperation with allies, not a capture operation involving U.S. forces or a kill order. But it does sometimes end up requiring delicate litigation over the suspect’s treatment abroad. For example, Ahmed Omar Abu Ali -- a young man from Virginia -- was arrested in Saudi Arabia for involvement with an al Qaeda cell. He was transferred some time later to U.S. custody to face trial for conspiring to, among other things, kill President George W. Bush. The major issue in his case was whether the highly incriminating statements he made in Saudi custody were voluntary or not. Deciding this question required, remarkably, testimony by Saudi intelligence officials who interrogated Abu Ali. Abu Ali was ultimately convicted and given a lengthy prison term.
7. When an Ally Won't Transfer

A girl is silhouetted against the setting sun as she sells national flags ahead of Pakistan's Independence Day, in Karachi.
At times, an ally will not transfer a suspect to U.S. jurisdiction, instead preferring to try him on its own. In December 2009, Pakistan arrested five American Muslims from the Washington, D.C. area who had traveled abroad for training and to fight U.S. soldiers by joining up with the Taliban. The United States sought their extradition, but Pakistan refused. In 2010, a Pakistani court found them guilty and sentenced them to 10 years in prison for conspiring against the Pakistani state.
An ally may wish to try Americans on its own for several reasons. They may be breaking local laws and could pose a real threat to the ally in question -- the ostensible reasons for trying them locally rather than extraditing them. Often more importantly, the trial allows the local government to claim politically that it is defending its own people and is doing so by going after unpopular foreigners rather than, in Pakistan’s case, taking on dangerous indigenous terrorists who enjoy more legitimacy and who have powerful allies in the country. In addition, refusing an extradition request is a way of standing up to the United States and gaining, or at least not losing, nationalist credibility.
From a U.S. point of view, it may be easier to let the ally do the work. From a counterterrorism point of view, these potentially dangerous individuals are off the street for a decade, while a trial in the U.S. is resource intensive and can be unpredicatable.
8. Do we care?

An armed guard of the deputy mayor of the central Somali town of Belet Weyne walks during an early morning foot patrol.
At times, authorities may suspect an individual overseas of involvement in terrorism yet not deem him dangerous enough to warrant any extensive intervention. Simply put, the individual is too minor to waste scarce military, financial, and other resources pursuing.
9. Can a Criminal Case Be Made?

The judge's gavel is seen in room 422 of the New York Supreme Court.
If an overseas suspect does not pose an imminent threat and is not operational -- and in general is considered low on the priority list -- then lethal force is off the table but U.S. officials may still examine whether they can successfully bring criminal charges. Elements of this calculation include whether important and classified sources and methods would be revealed and the strength of the legal (as opposed to intelligence) case. Officials recognize, however, that the suspect is not likely to show up for trial and that the indictment is in some ways just a placeholder for further action if circumstances change.
10. The Plausibility of Capture

Attorney General Eric Holder holds a press conference at the Department of Justice in Washington
If the suspect is someone officials care about enough to take action against, they face another question: can they catch him? Capture operations are difficult and dangerous, and like targeting operations, they require knowing exactly where the suspect will be at the right time. Authorities might not tolerate Adam Gadahn, a senior al Qaeda spokesman and advisor to Ayman Al-Zawahiri, if they were able to locate him in a place where they could conduct a capture operation with tolerable risks to U.S. military or covert forces.
We know of no post-9/11 case in which authorities have launched an overseas capture operation against a U.S. national, though there have been several cases -- for example, John Walker Lindh and Yasser Hamdi -- in which U.S. nationals have been swept up along with other captured enemy forces. Still, Attorney General Eric Holder specifically included the question of whether capture was “implausible” as a deciding factor in a speech addressing the appropriate times to use lethal force on U.S. nationals overseas. Following the administration’s rubric, any person captured would necessarily be routed into the domestic criminal justice system.
11. The operations question

Anwar al-Awlaki, a U.S.-born cleric linked to al Qaeda's Yemen-based wing, gives a religious lecture from an unknown location.
U.S. officials draw a sharp distinction between propagandists like Gadahn and people like Padilla or even the DC-Five, who planned or were potentially directly involved in operations. In theory, it is operators who matter: words do not kill, or at least not directly, while someone willing to pick up a gun or plant a bomb leaves little doubt about his bloody plans.
Propagandists, to some degree, are also protected under U.S. law. Glorifying jihad and saying that Americans fighting in Iraq and Afghanistan, or even living ordinary lives stateside, deserve death, is not in itself a crime. So even Anwar al-Awlaki, who inspired Americans and Western Muslims in general to take up jihad, was not aggressively targeted until he was linked to attacks on U.S. airlines and aviation targets in the United Kingdom -- thus going from “propagandist” to “operator.” Non-operational figures abroad -- however dangerous -- will tend to be tolerated to the extent they cannot be captured.
12. The Imminent Threat

A woman is reflected in a threat advisory notice in Washington.
Not even all operational figures can be lawfully targeted with lethal force. Holder’s speech only defends as lawful the targeting of a senior operational figure who cannot be captured when he poses an imminent threat to the United States -- though Holder holds open the possibility targeting might satisfy the law in a broader range of circumstances.
The United States uses the word “imminent” in a looser fashion than its colloquial meaning suggests -- not to refer to an inevitable immediate threat (a bomb going off tomorrow) but to an unfolding chain of events that, left uninterrupted, will produce dead Americans. Even this understanding of imminence, however, leaves another gap: the operational leader who poses a non-imminent threat. This may be an empty set, but that group of people would also seem to fall into a zone of de facto tolerance.
13. Target with Lethal Force

File photo of a Predator drone above the U.S.S. Carl Vinson.
In practice, the United States has targeted with lethal force only one of its own citizens: Anwar al-Awlaki. Three others, including Awlaki’s teenage son and propagandist Samir Khan, have been killed in drone strikes, but none of them appears to have been the target of the strike; all were considered collateral damage.
14. Indict and Tolerate

File video grab of American al Qaeda militant Adam Gadahn speaking.
Sometimes, the United States will simply indict a low-priority individual but then do little else. Adam Gadahn is perhaps the best example of this today. The Justice Department indicted him in 2005 for “providing material support” for al Qaeda, a broad charge regularly used in terrorism cases. In 2006, Gadahn was charged with treason, the first American so-charged in over 50 years. Yet these seemingly strong actions belie an obvious limit: Gadahn is outside U.S. and allied control, and his arrest does not appear to be an operational priority, though officials would certainly welcome it should it occur.
15. Ignore and Wait

Men suspected to be from al Shabaab are guarded at former police station by soldiers of SNA in the southern Somali port city of Kismayu.
The United States may choose not go after a suspected terrorist because officials believe he poses at most a minor threat to the United States. They’re not going to make a significant effort to push allies to nab him or to deploy U.S. overseas assets to do so. In practice, many such individuals primarily pose threats to an ally rather than to U.S. citizens or institutions. For example, Daniel Maldonado traveled to Somalia in 2005 to wage jihad on behalf of al Shabaab, a Somali jihadist group. When Kenya invaded Somalia in 2007, Maldonado was turned over to the United States, but the Bush administration had not actively pursued him before Kenya captured him. Maldonado was helping a noxious Somali group, but he was simply one soldier among thousands, and at the time al Shabaab was less tied to al Qaeda than it is today.